Introduction
The LAMP stack is a bundle consisting of a Linux operating system, an Apache server, a MySQL (MariaDB) database, and the PHP programming language. Each layer of the stack represents an open-source software required for developing web applications.
In this tutorial you will learn how to install the LAMP stack on CentOS 7.

Note: If you are running a newer release of CentOS, refer to How to Install LAMP Stack on CentOS 8.
Prerequisites
- Access to a user account with sudo or root privileges
- A terminal window or command line
- The yum and RPM package managers, included by default
Step 1: Update Package Repository Cache
Before you start building the stack, be sure to update the packages on your CentOS 7 server using the command:
sudo yum updateStep 2: Install the Apache Web Server
As you already have a CentOS operating system running, the first step of assembling the LAMP stack is to install the web server. The simplest way to install Apache is through CentOS’s native package manager, yum.
1. Install Apache on Centos with:
sudo yum install httpdWhen prompted, confirm that you are executing the command with sudo privileges.
The output will show the package httpd package was installed as in the image below:
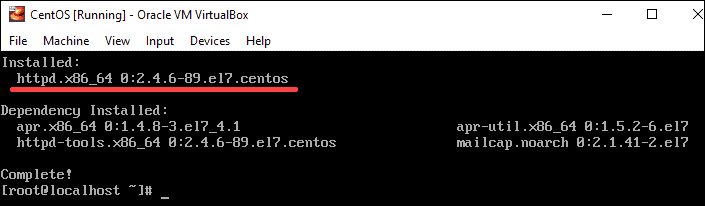
2. Next, start Apache by running the following command:
sudo systemctl start httpd.service3. Check whether the service is running by going to your server’s public IP address. The browser should display the test CentOS 7 Apache web page:
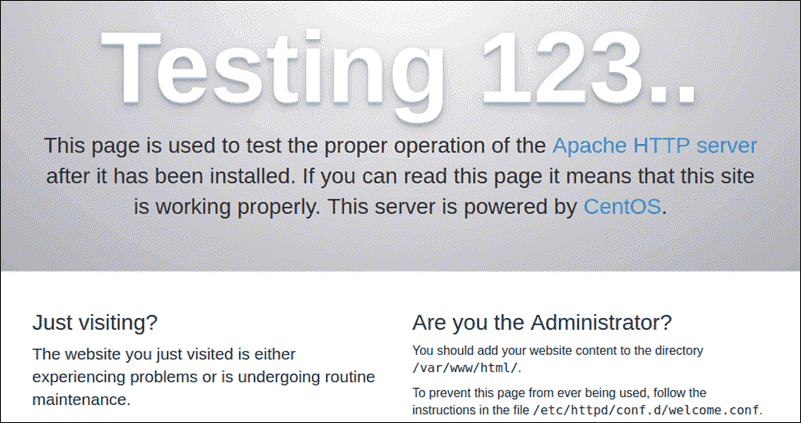
4. Finally, set up Apache to start at boot:
sudo systemctl enable httpd.serviceStep 3: Install MySQL (MariaDB) and Create a Database
To organize and store data for your dynamic website, you need MariaDB. This is an open-source fork of the MySQL database management system. It is a backward compatible and binary drop-in replacement for the original MySQL.
1. Install MariaDB with the command:
sudo yum install mariadb-server mariadbWhen a y/n prompt appears, confirm with y.
2. Now start MariaDB using the command:
sudo systemctl start mariadbStep 4: Run MySQL Security Script
MariaDB does not have secure settings by default. Therefore, you need to configure settings, test the database, and remove anonymous users.
1. Begin by typing the command:
sudo mysql_secure_installation2. You will be prompted to provide your MariaDB root password (this is not the root password for your server). As you do not have a password yet, pressing Enter allows you to continue configuration.
3. Next, it will ask you a series of queries. To ensure your database is protected, answer the questions as follows:
- Set root password? [y/n] Y
- New password: Type in a password you would like to use
- Re-enter new password: Retype the password from the previous field
- Remove anonymous users? [y/n] Y
- Disallow root login remotely? [y/n] Y
- Remove test database and access to it? [y/n] Y
- Reload privilege tables now? [y/n] Y
4. After answering the questions, the output will display a message that your system is cleaning up, and the installation should now be secure.
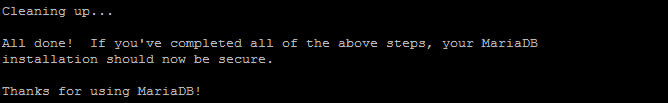
5. Lastly, enable MariaDB to start up when you boot the system:
sudo systemctl enable mariadb.serviceStep 5: Install PHP
As a server-side scripting language, PHP is the part of the LAMP grouping that processes the code for showing dynamic content. Once it is connected with the MySQL database, PHP will be retrieving information and processing it for the Apache webserver to display.
1. Install the MySQL extension along with PHP, again using the yum package installer, with the command:
sudo yum install php php-mysqlNow you should get a Y/n prompt allowing you to confirm the installation, by entering Y.
2. To have your Apache webserver start co-working with PHP, restart the server:
sudo systemctl restart httpd.service Step 6: Test PHP Processing
To locate and serve the website, Apache must save the file to the web root. Apache places its default website in this directory: /var/www/html/
By using the nano editor, you can go into this directory and run a test of PHP on the CentOs 7 server.
1. To install the editor, use this command:
sudo yum install nano2. Use a basic PHP script to make an info.php file, with the command:
sudo nano /var/www/html/info.php3. This opens a blank text file in which you should copy and paste the following:
<?php
phpinfo ();
?>
4. Hold CTRL+X (to exit) and Y and Enter (to save changes, and close the file).
5. Check whether PHP is working by visiting the following URL:
http://ip_address/info.phpThe ip_address should be the public IP address of your server. If PHP is set up correctly you will see this image on the browser:
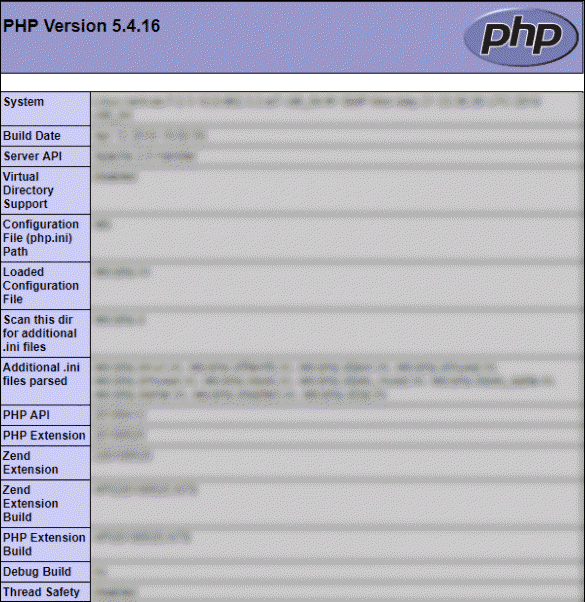
6. If a firewall is enabled you will need to open a route for HTTP traffic. Use the command:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=httpFollowing with the command to open it for HTTPS traffic:
sudo firewall-cmd --permanent --zone=public --add-service=httpsFinally, restart the firewall to enable the new settings:
sudo firewall-cmd --reloadStep 7: Install PHP Modules
To optimize PHP’s capabilities, look at the names and descriptions of optional modules with the command:
yum search php-To get detailed, plain-language information about what each module does, view a longer description with: yum info followed by a space and the module name.
Install an optional package with sudo yum install followed by a space and the module name.
Step 8: Restart Apache
In order for the changes to take effect, restart the Apache service with the command:
sudo systemctl restart apache2Conclusion
By following this guide, you learned how to install each layer of the LAMP stack on CentOS. Now you are ready to explore all the innovations the LAMP stack makes possible.