Introduction
When files in a package are modified or accidentally removed, it can damage the system. Installing the package again resolves the problem in most cases. However, using the apt-get install command will return an error, given that the package is already present.
The --reinstall flag is a shortcut for an apt-get command used to reinstall packages, using the most up-to-date versions. This is useful for packages with many reverse dependencies.
In this tutorial you will learn how to use apt-get reinstall to reinstall packages on Debian and Ubuntu.
Note: Using the --purge remove option to remove packages and installing them again achieves similar results. However, it also erases configuration files.
Prerequisites
- An account with sudo privileges
- Access to the command line/ terminal
- A Debian/Ubuntu system
Reinstall Packages Using apt-get
Using the --reinstall command is a simple process. The syntax is as follows:
sudo apt-get --reinstall install PackageNameIf you wish to reinstall more than one package, you can list them all in one line:
sudo apt-get --reinstall install PackageName1 PackageName2Reinstall htop Using apt-get
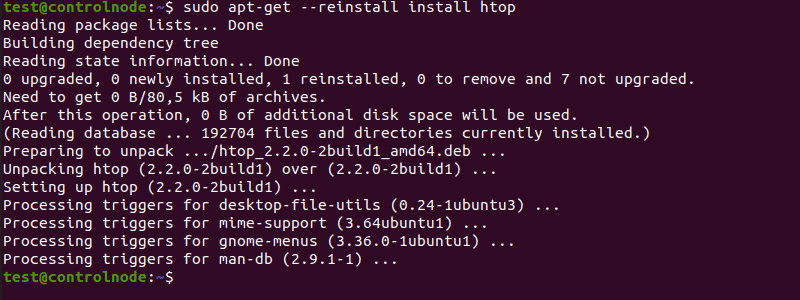
This is how to reinstall htop, an interactive process viewer on Ubuntu, using the --reinstall flag.
sudo apt-get --reinstall install htopThe output should look like this:
Reinstall Packages Using aptitude Command
Aptitude is a graphical user interface for the apt package manager. However, it can be used with the command line too.
If you wish to reinstall a package with aptitude, use the following syntax:
sudo aptitude reinstall PackageName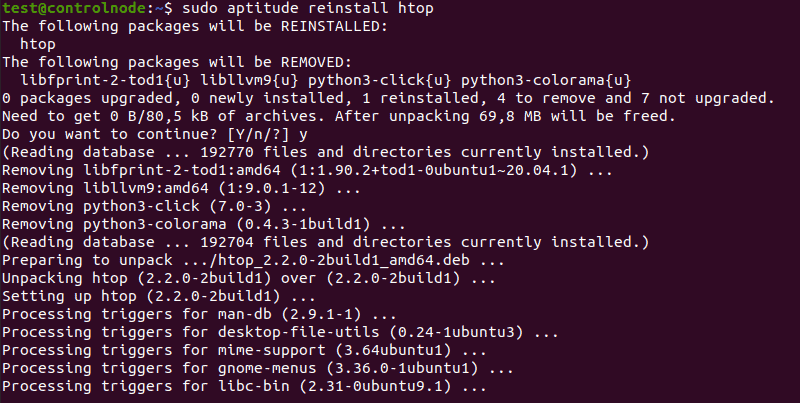
Note: Use sudo aptitude reinstall '~i' command if you wish to reinstall ALL packages.
Reinstall apt After You Accidentally Removed It
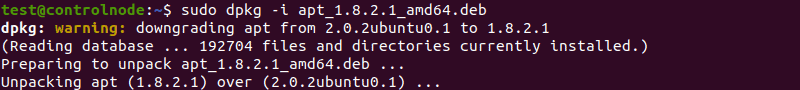
If you accidentally remove apt, for example by purging it using --force-* option, install it again in three simple steps:
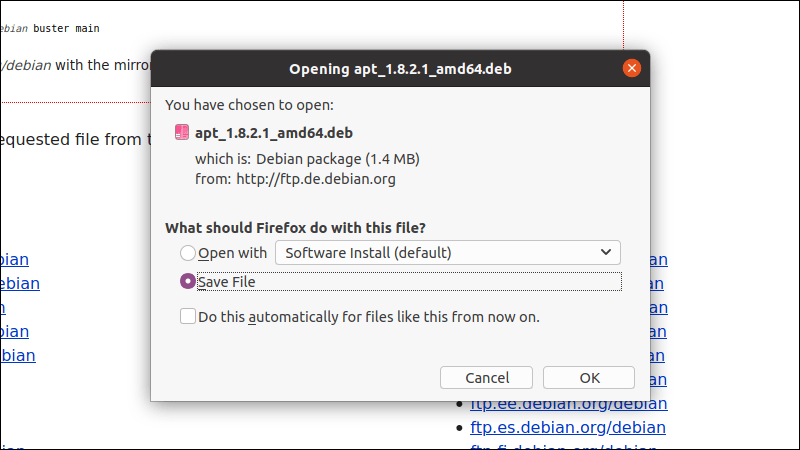
1. Go to https://packages.debian.org/apt to search for the release of your choice. Avoid testing or unstable releases.
2. Choose the version number and download the package for your architecture.
3. In terminal, run:
sudo dpkg -i apt_0.5.4_i386.debReplace the version and architecture in the example as necessary.
Conclusion
After reading this article, you should be able to reinstall packages using both apt-get and aptitude commands, as well as to restore apt itself if it is removed accidentally.
For more details on the apt package manager, read our article on how to manage packages on Ubuntu.